Economy of the European Union
Background to the schools Wikipedia
SOS Children, which runs nearly 200 sos schools in the developing world, organised this selection. SOS Children is the world's largest charity giving orphaned and abandoned children the chance of family life.
| Economy of the European Union | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Currency | 1 Euro (€) = 100 cents |
|
Other currencies in member states |
|
| Statistics | |
| GDP ranking | 1st (2011) |
| GDP ( Nominal) | US$17.578 trillion (2011) €12.629 trillion (2011) |
| GDP ( PPP) | US$15.821 trillion (2011) |
| GDP growth rate | 1.5% (2011) |
| GDP per capita | US$35,116 (nominal) US$31,607 ( PPP) (2011) |
| GDP by sector (2006) | 70.5% services 27.3% industry 2.1% agriculture |
| Inflation | 2.6 % (2012) |
| Population below poverty threshold | 17% |
| Labour force | 240.2 million |
| Labour force by occupation (2011) | 69.8% services 25.2% industry 5.0% agriculture |
| Unemployment | 10.8% (January 2013) |
| Sources:
|
|
| Trading partners | |
| Export of goods | €1.531 trillion (2011) $2.131 trillion (2011) |
| Export of services | €579.5 billion (2011) $806.6 billion (2011) |
|
Export goods (2011) |
|
|
Main export partners (2011) |
|
| Import of goods | €1.685 trillion (2011) $2.344 trillion (2011) |
| Import of services | €470.4 billion (2011) $654.8 billion (2011) |
|
Import goods (2011) |
|
|
Main import partners (2011) |
|
| FDI inward stock | € 3.806 trillion (2011) |
| FDI outward stock | € 4.983 trillion (2011) |
| Sources: | |
| Balance of Payments | |
| Current Account | € 61.537 billion (2012) |
| Sources: | |
| Public finances | |
| Public debt | € 10,421.9 billion (82.5% of GDP) (2011) |
| Public deficit | € -565.1 billion (-4.5% of GDP) (2011) |
| Expenditure | 49.1% of GDP (2011) |
| Revenue | 44.6% of GDP (2011) |
| Sources: | |
The economy of the European Union generates a GDP of over €12.629 trillion (US$17.578 trillion in 2011) according to the International Monetary Fund (IMF), making it the largest economy in the world. The European Union (EU) economy consists of an Internal Market and the EU is represented as a unified entity in the World Trade Organization (WTO).
Currency
The official currency of the European Union is the euro used in all its documents and policies. The Stability and Growth Pact sets out the fiscal criteria to maintain for stability and (economic) convergence. The euro is also the most widely used currency in the EU, which is in use in 17 member states known as the Eurozone.
All other member states, apart from Denmark and the United Kingdom, which have special opt-outs, have committed to changing over to the euro once they have fulfilled the requirements needed to do so. Also, Sweden can effectively opt out by choosing when or whether to join the European Exchange Rate Mechanism, which is the preliminary step towards joining. The remaining states are committed to join the Euro through their Treaties of Accession.
Budget
The operation of the EU has an agreed budget of €141 billion for the year 2011, and €862 billion for the period 2007–2013, this represents around 1% of the EU's GDP.
Economic variation
Below is a table showing, respectively, the GDP and the GDP (PPP) per capita for the European Union and for each of its 27 member states, sorted by GDP (PPP). This can be used as a rough gauge to the relative standards of living among member states, with Luxembourg the highest and Bulgaria the lowest. Eurostat, based in Luxembourg, is the Official Statistical Office of the European Communities releasing yearly GDP figures for the member states as well as the EU as a whole, which are regularly updated, supporting this way a measure of wealth and a base for the European Union's budgetary and economic policies. Figures are stated in euro.
| Member states | GDP 2011 millions of euro |
Population in millions |
GDP (PPP) per capita 2011 euro |
GDP (Nominal) per capita 2011 euro |
GDP (PPP) per capita 2011 EU27 = 100 |
Eurozone yes/no |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12,650,983 | 501 | 25,200 | 25,200 | 100% | ||
| 2,592,600 | 81.4 | 30,300 | 31,700 | 121% | yes | |
| 1,996,583 | 63.3 | 27,200 | 30,600 | 108% | yes | |
| 1,750,396 | 62.6 | 27,400 | 27,900 | 109% | no | |
| 1,579,659 | 61.5 | 25,100 | 26,000 | 100% | yes | |
| 1,063,355 | 46.0 | 24,700 | 23,100 | 98% | yes | |
| 601,973 | 16.6 | 32,900 | 36,100 | 131% | yes | |
| 387,596 | 9.3 | 31,900 | 41,100 | 127% | no | |
| 369,836 | 10.8 | 29,900 | 33,700 | 119% | yes | |
| 369,666 | 38.2 | 16,200 | 9,600 | 64% | no | |
| 300,712 | 8.4 | 32,400 | 35,700 | 129% | yes | |
| 240,453 | 5.5 | 31,500 | 43,200 | 125% | no | |
| 208,532(p) | 11.3 | 20,100(p) | 18,500(p) | 79% | yes | |
| 189,368 | 5.3 | 28,800 | 35,200 | 114% | yes | |
| 171,040(p) | 10.6 | 19,500(p) | 16,100(p) | 77% | yes | |
| 156,438 | 4.4 | 32,500 | 35,400 | 129% | yes | |
| 156,217 | 10.5 | 20,200 | 14,900 | 80% | no | |
| 131,327 | 21.5 | 11,400(2010) | 5,800(2010) | 49% | no | |
| 99,819 | 10.0 | 16,500 | 10,000 | 66% | no | |
| 69,108 | 5.4 | 18,400 | 12,700 | 73% | yes | |
| 42,625 | 0.5 | 68,100 | 82,100 | 271% | yes | |
| 38,483 | 7.6 | 11,600 | 5,200 | 46% | no | |
| 36,172 | 2.0 | 21,000 | 17,600 | 84% | yes | |
| 30,807 | 3.2 | 16,600 | 10,200 | 66% | no | |
| 20,211 | 2.2 | 14,700 | 9,800 | 58% | no | |
| 17,979 | 0.8 | 23,700 | 21,100 | 94% | yes | |
| 15,951 | 1.3 | 16,900 | 11,900 | 67% | yes | |
| 6,544 | 0.4 | 21,500 | 15,600 | 85% | yes |
| EU Candidates | GDP 2011 millions of euro |
Population in millions |
GDP (PPP) per capita 2011 euro |
GDP (Nominal) per capita 2011 euro |
GDP (PPP) per capita 2011 perc. of EU27 |
Eurozone yes/no |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10,075 | 0.3 | 28,000 | 31,600 | 111% | no | |
| 44,893(p) | 4.5 | 15,400(p) | 10,500(p) | 61% | no | |
| 553,249 | 71.0 | 13,100 | 7,500 | 52% | no | |
| 7,509 | 2.0 | 8,700(2010) | 3,400(2010) | 35% | no | |
| 0.6 | 42% | no | ||||
| 34,740 | 7.3 | 8,800 | 4,686 | 35% | no |
| Current EU applicants | GDP 2010 millions of euro |
Population in millions |
GDP (PPP) per capita 2011 euro |
GDP (Nominal) per capita 2009 euro |
GDP (PPP) per capita 2011 perc. of EU27 |
Eurozone yes/no |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8,975 | 3.2 | 7,800(e) | 2,803 | 30% | no | |
| 3.8 | 7,300 | 30% | no |
| EFTA members | GDP 2010 millions of euro |
Population in millions |
GDP (PPP) per capita 2011 euro |
GDP (Nominal) per capita 2011 euro |
GDP (PPP) per capita 2011 perc. of EU27 |
Eurozone yes/no |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 352,856 | 4.6 | 47,500 | 70,500 | 186% | no | |
| 476,054 | 7.7 | 39,500 | 60,800 | 157% | no |
p: provisional value
e: estimated value
Source: GDP Millions of PPS: EUROSTAT, GDP(PPP) per inhabitant: EUROSTAT, GDP per capita in PPS : EUROSTAT, GDP per capita expressed in PPS in percentage of EU (2011): EUROSTAT
| Past and future GDP at market prices (millions of euro)[nb 1] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Economies of member states
Economic performance varies from state to state. The Growth and Stability Pact governs fiscal policy with the European Union. It applies to all member states, with specific rules which apply to the eurozone members that stipulate that each state's deficit must not exceed 3% of GDP and its public debt must not exceed 60% of GDP. However, many larger members have consistently run deficits substantially in excess of 3%, and the eurozone as a whole has a debt percentage exceeding 60% (see below).
The following table shows information relating to the member states of the European Union, ordered according to the 'Size' of their economies. (NB: Were the table ordered according to 'GDP per capita' this would perhaps better reflect the strength of an individual economy. But this is not how such tables are commonly structured.) The colours denote how a member state is performing relative to the rest of the European Union, above average (green) or below average (red). The smallest and greatest values in each column are emphasised.
The data for GDP and GDP per capita (PPP) are based on the World Economic Outlook, October 2012 ( International Monetary Fund).
| Member State sorted by GDP |
GDP in billions of USD (2011) |
GDP % of EU (2010) |
Annual change % of GDP (2011) |
GDP per capita in PPP US$ (2011) |
Public Debt % of GDP (Q3 2012) |
Deficit (-)/ Surplus (+) % of GDP (2011) |
Inflation % Annual (2011) |
Unemp. % 2012 M12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 17,610.8 | 100.0 | 1.5 | 31,673 | 85.1 | -4.5 | 3.1* | 10.8 | |
| 3,607.4 | 20.2% | 3.0 | 38,077 | 81.7 | -1.0 | 2.5 | 5.3 | |
| 2,778.1 | 15.8% | 1.8 | 35,068 | 85.8 | -5.2 | 2.3 | 10.6 | |
| 2,431.3 | 13.9% | 0.8 | 36,522 | 89.9 | -8.3 | 3.3* | 7.7* | |
| 2,198.7 | 12.7% | 0.4 | 30,464 | 127.3 | -3.9 | 2.9 | 11.7 | |
| 1,479.6 | 8.7% | 0.7 | 30,478 | 77.4 | -8.5 | 3.1 | 26.2 | |
| 838.1 | 4.8% | 1.2 | 42,023 | 69.5 | -4.7 | 2.5* | 6.0 | |
| 514.5 | 2.9% | 4.3 | 20,184 | 55.9 | -5.1 | 3.9 | 10.6 | |
| 514.6 | 2.9% | 1.9 | 37,781 | 101.6 | -3.7 | 3.5 | 7.4 | |
| 544.7 | 2.8% | 3.9 | 40,705 | 37.4 | 0.3 | 1.4 | 8.0 | |
| 418.4 | 2.3% | 3.1 | 41,556 | 73.7 | -2.6 | 3.6* | 4.9 | |
| 333.0 | 1.9% | 1.0 | 37,048 | 47.5 | -1.8 | 2.7 | 7.4 | |
| 399.3 | 1.9% | -6.8 | 26,258 | 152.6 | -9.8 | 3.1 | 27.0* | |
| 263.5 | 1.5% | 2.9 | 35,981 | 51.1 | -0.5 | 3.3 | 7.9 | |
| 237.8 | 1.4% | -1.6 | 23,363 | 120.3 | -4.2 | 3.6 | 17.6 | |
| 221.2 | 1.3% | 0.9 | 40,838 | 117.0 | -13.1 | -1.6* | 14.7 | |
| 215.2 | 1.2% | 1.7 | 27,063 | 44.9 | -3.1 | 2.1 | 7.0 | |
| 189.8 | 1.0% | 2.5 | 12,493 | 35.2 | -5.2 | 5.8 | 6.6 | |
| 140.3 | 0.8% | 1.7 | 19,591 | 78.6 | 4.3 | 3.9 | 11.1 | |
| 96.1 | 0.5% | 3.3 | 23,304 | 51.2 | -4.8 | 4.1 | 14.9 | |
| 59.6 | 0.3% | 1.1 | 80,559 | 20.9 | -0.6 | 3.7 | 5.3 | |
| 53.5 | 0.3% | 1.7 | 13,789 | 18.7 | -2.1 | 3.4 | 12.4 | |
| 50.3 | 0.3% | -0.2 | 28,843 | 48.2 | -6.4 | 2.1 | 10.2 | |
| 42.7 | 0.2% | 5.9 | 19,125 | 40.6 | -5.5 | 4.1 | 13.3 | |
| 28.3 | 0.1% | 5.5 | 16,818 | 40.4 | -3.5 | 4.2 | 14.4* | |
| 24.7 | 0.1% | 0.5 | 27,521 | 84.0 | -6.3 | 3.5 | 14.7 | |
| 22.2 | 0.1% | 7.6 | 20,379 | 9.6 | 1.0 | 5.1 | 9.9* | |
| 8.9 | 0.1% | 2.1 | 25,598 | 73.1 | -2.7 | 2.4* | 7.0 |
Economic growth
The EU's share of Gross world product (GWP) is stable at around one fifth.
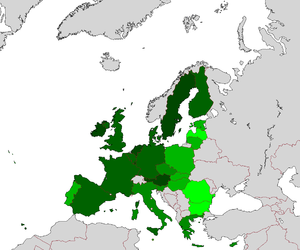
The twelve new member states of the European Union have enjoyed a higher average percentage growth rate than their elder members of the EU. Slovakia has the highest GDP growth in the period 2005-2011 among all countries of the European Union (See Tatra Tiger). Notably the Baltic states have achieved massive GDP growth, with Latvia topping 11%, close to China, the world leader at 9% on average for the past 25 years (though these gains have been in great part cancelled by the late-2000's recession).
Reasons for this massive growth include government commitments to stable monetary policy, export-oriented trade policies, low flat-tax rates and the utilisation of relatively cheap labour. For the last year (2011), Estonia had the highest GDP growth from all the states in EU (7,6%). The current map of EU growth is one of huge regional variation, with the larger economies suffering from stagnant growth and the new nations enjoying sustained, robust economic growth.
Although EU27 GDP is on the increase, the percentage of Gross world product is decreasing due to the emergence of economic powers such as China, India and Brazil. In the medium to long term, the EU will be looking forward to increase GDP growth in Italy and the UK in order to stabilise growth in European Union states. This is to ensure sustained economic prosperity.
Trade
EU imports, exports and balance of trade in goods from 2007 to 2011 (in billions of euro)

EU current account(quarterly data ) in millions of euro.
The European Union is the largest exporter in the world and as of 2008 the largest importer of goods and services. Internal trade between the member states is aided by the removal of barriers to trade such as tariffs and border controls. In the eurozone, trade is helped by not having any currency differences to deal with amongst most members. The European Union Association Agreement does something similar for a much larger range of countries, partly as a so-called soft approach ('a carrot instead of a stick') to influence the politics in those countries. The European Union represents all its members at the World Trade Organization (WTO), and acts on behalf of member states in any disputes. When the EU negotiates trade related agreement outside the WTO framework, the subsequent agreement must be approved by each individual EU member.
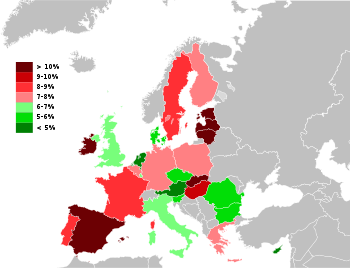
UnemploymentThe seasonally adjusted unemployment rate in the European Union (EU27) in March 2009 was 8.3% compared to 6.7% in March 2008. The Eurozone (EA16) unemployment figure for January 2009 was 8.2% compared to 7.3% in January 2008. The unemployment rate (EU25) had previously declined in prior years from 8.9% in March 2005 to 8.4% in March 2006 to 7.3% in March 2007. The rate varies widely by member state. There has been a steep upturn in the unemployment rate since 2008 due to the worldwide credit crunch and following recession. The countries within the EU which were most affected were Spain, Ireland and the Baltic countries with the unemployment rate doubling or in case of the Baltic countries nearly tripling. By comparison in March 2009 the United States had an unemployment rate of 8.6% (2008: 5.1; 2007: 4.4; 2006: 4.7) which was higher than the EU-27's unemployment rate but lower than the EU-16 Eurozone rate of 8.9%. Japan's unemployment rate remained comparatively steady at 4.4% (2008: 3.9; 2007: 4.0; 2006: 4.1). The following tables show the current unemployment rate of all Member States for March 2009 with comparisons to March 2008, 2007, 2006 and 2005 and comparisons to the United States and Japan:
IndustriesThe services sector is by far the most important sector in the European Union, making up 69.4% of GDP, compared to the manufacturing industry with 28.4% of GDP and agriculture with only 2.3% of GDP. AgricultureThe agricultural sector is supported by subsidies from the European Union in the form of the Common Agricultural Policy (CAP). This currently represents 40–50% of the EU's total spending. It guarantees a minimum price for farmers in the EU. This is criticised as a form of protectionism, inhibiting trade, and damaging developing countries; one of the most vocal opponents is the UK, the third largest economy within the bloc, which has repeatedly refused to give up the annual UK rebate unless the CAP undergoes significant reform; France, the biggest benefactor of the CAP and the bloc's second largest economy, is its most vocal proponent. TourismThe European Union is a major tourist destination, attracting visitors from outside of the Union and citizens travelling inside it. Internal tourism is made more convenient for the citizens of some EU member states by the Schengen treaty and the Euro. All citizens of the European Union are entitled to travel to any member state without the need of a visa. France is the world's number one tourist destination for international visitors, followed by Spain, Italy and the United Kingdom at 2nd, 5th and 6th spots respectively. It is worth noting however a significant proportion of international visitors to EU countries are from other member states. London, the capital of the United Kingdom is also the world's most visited city and the highest in tourism receipts, before Paris. CompaniesThe European Union's member states are the birthplace of many of the world's largest leading multinational companies, and home to its global headquarters. Among these are distinguished companies ranked first in the world within their industry/sector, like Allianz, which is the largest financial service provider in the world by revenue; WPP plc which is the world's largest advertising agency by revenue; Airbus, which is the world's largest aircraft manufacturer; Air France-KLM, which is the largest airline company in the world in terms of total operating revenues; Amorim, which is the world's largest cork-processing and cork producer company; ArcelorMittal, which is the largest steel company in the world; Inditex which is the biggest fashion group in the world; Groupe Danone, which has the world leadership in the dairy products market. Anheuser-Busch InBev is the largest beer company in the world; L'Oréal Group, which is the world's largest cosmetics and beauty company; LVMH, which is the world's largest luxury goods conglomerate; Nokia Corporation, which is the world's largest manufacturer of mobile telephones; Royal Dutch Shell, which is one of the largest energy corporations in the world; and Stora Enso, which is the world's largest pulp and paper manufacturer in terms of production capacity, in terms of banking and finance the EU has some of the worlds largest notably HSBC and Grupo Santander, the largest bank in Europe in terms of Market Capitalisation. Many other European companies rank among the world's largest companies in terms of turnover, profit, market share, number of employees or other major indicators. A considerable number of EU-based companies are ranked among the worlds' top-ten within their sector of activity. Europe is also home to many prestigious car companies such as Audi, Mercedes, Jaguar Land Rover, Volkswagen, BMW group as well as volume manufacturers such as Fiat, PSA group and Renault. Gini indexTo date, one of the most commonly used measures of income inequality is the Gini index. The Gini coefficient measures income inequality on a scale from 0 to 1. On this scale 0 represents perfect equality with everyone having exactly the same income and 1 represents perfect inequality with one person having all income. According to the UN (UN), Gini index ratings for countries range from 0.247 in Denmark to 0.743 in Namibia. Most post-industrial nations had a Gini coefficient in the range 0.25 to 0.40. In 2005 the Gini index for the EU was estimated at 0.31 and as a comparison the USA had 0.463. Regional variationComparing the richest areas of the EU can be a difficult task. This is because the NUTS 1 & 2 regions are not homogenous, some of them being very large regions, such as NUTS-1 Hesse (21,100 km²) or NUTS-1 Île-de-France (12,011 km²), whilst other NUTS regions are much smaller, for example NUTS-1 Hamburg (755 km²) or NUTS-1 Greater London (1,580 km²). An extreme example is Finland, which is divided for historical reasons into mainland Finland with 5.3 million inhabitants and Åland, an autonomous archipelago with a population of 27,000, or about the population of a small Finnish city. One problem with this data is that some areas, including Greater London, are subject to a large number of commuters coming into the area, thereby artificially inflating the figures. It has the effect of raising GDP but not altering the number of people living in the area, inflating the GDP per capita figure. Similar problems can be produced by a large number of tourists visiting the area. The data is used to define regions that are supported with financial aid in programs such as the European Regional Development Fund. The decision to delineate a Nomenclature of Territorial Units for Statistics (NUTS) region is to a large extent arbitrary (i.e. not based on objective and uniform criteria across Europe), and is decided at European level (See also: Regions of the European Union). Top 10: economically strongest NUTS-1 and NUTS-2 regionsThe 10 NUTS-1 and NUTS-2 regions with the highest GDP per capita are almost all, except two, in the first fifteen member states: Prague and Bratislava are the only ones in the 12 new member states that joined in May 2004 and January 2007. The leading regions in the ranking of NUTS-2 regional GDP per inhabitant in 2008 were Inner London in the United Kingdom (343% of the average), the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg (279%) and Bruxelles/Brussels in Belgium (216%). Figures for these three regions, however, are artificially inflated by the commuters who do not reside in these regions ("Net commuter inflows in these regions push up production to a level that could not be achieved by the resident active population on its own. The result is that GDP per inhabitant appears to be overestimated in these regions and underestimated in regions with commuter outflows."). Another example of artificial inflation is Groningen. The calculated GDP per capita is very high due to the large natural gas reserves in this region. However, Groningen is in fact one of the poorest parts in the Netherlands. Among the 40 NUTS-2 regions exceeding the 125% level, ten were in Germany, five in the Netherlands, four each in Austria and United Kingdom, three each in Spain and Italy, two each in Belgium and Finland, one each in the Czech Republic, Denmark, Ireland, France, Slovakia and Sweden, as well as the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg. The NUTS Regulation lays down a minimum population size of 3 million and a maximum size of 7 million for the average NUTS-1 region, whereas a minimum of 800,000 and a maximum of 3 million for NUTS-2 regions ¹ . This definition, however, is not respected by Eurostat. E.g.: the région of Île-de-France, with 11.6 million inhabitants, is treated as a NUTS-2 region, while the state of Bremen, with only 664,000 inhabitants, is treated as a NUTS-1 region.
Source: Eurostat Economically weakest NUTS-2 regionsThe twenty lowest regions in the ranking in 2008 were all in Bulgaria, Romania, Poland and Hungary, with the lowest figures recorded in Severozapaden in Bulgaria (27% of the average), followed by Nord-Est (29%) in Romania, Severen tsentralen in Bulgaria (29%) and Yuzhen tsentralen in Bulgaria (31%). Among the 64 regions below the 75% level, fifteen were in Poland, seven each in the Czech republic and Romania, six each in Bulgaria and Hungary, four each in Italy and Portugal, three each in Greece, France (all overseas departments) and Slovakia, two in the United Kingdom, one in Spain, as well as Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania.
Source: Eurostat Richest & Poorest NUTS Regions (GDP PPP 2009)
Source: Eurostat |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||