 |
This is a file from the Wikimedia Commons. Information from its description page there is shown below.
Commons is a freely licensed media file repository. You can help.
|
Summary
| DescriptionNeuronResistanceCapacitanceRev.jpg |
|
| Date |
13 September 2006 (according to EXIF data) |
| Source |
Own work |
| Author |
User:Michael Klausen |
 |
This image was uploaded in the JPEG format even though it consists of non-photographic data. This information could be stored more efficiently or accurately in the PNG format or SVG format. If possible, please upload a PNG or SVG version of this image without compression artifacts, derived from a non-JPEG source (or with existing artifacts removed). After doing so, please tag the JPEG version with {{ Superseded|NewImage.ext}}, and remove this tag. This tag should not be applied to photographs or scans. For more information, see {{ BadJPEG}}. |
|
|
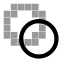 |
This image could be recreated using vector graphics as an SVG file. This has several advantages; see Commons:Media for cleanup for more information. If an SVG form of this image is already available, please upload it. After uploading an SVG, replace this template with {{ vector version available|new image name.svg}}. |
Licensing
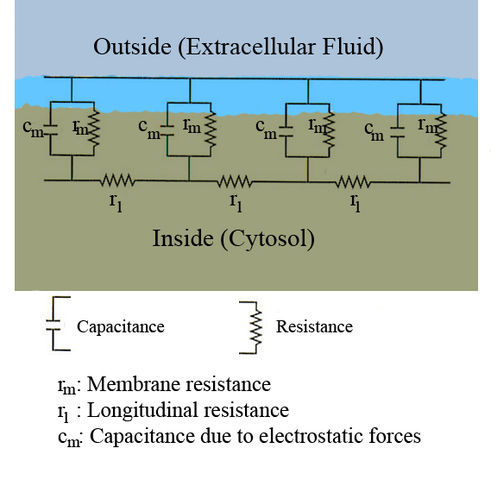
Schematic overview of cable theory's simplified view of a piece of neuronal fiber. When an electrical current is moving along the inside of a fibre the cytosol exerts a resistance (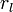 ). Simultaneously current will escape through the phospholipid bilayer (with resistance
). Simultaneously current will escape through the phospholipid bilayer (with resistance 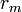 ) to the outside; and due to electrostatic forces a buildup of charge (
) to the outside; and due to electrostatic forces a buildup of charge (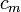 ) will take place along the bilayer.
) will take place along the bilayer.
| Public domainPublic domainfalsefalse |
 |
This work has been released into the public domain by its author, Michael Klausen. This applies worldwide.
In some countries this may not be legally possible; if so:
Michael Klausen grants anyone the right to use this work for any purpose, without any conditions, unless such conditions are required by law.Public domainPublic domainfalsefalse
|
File usage
The following pages on Schools Wikipedia link to this image (list may be incomplete):
This file contains additional information, probably added from the digital camera or scanner used to create or digitize it. If the file has been modified from its original state, some details may not fully reflect the modified file.
All five editions of Schools Wikipedia were compiled by SOS Children's Villages. More than 2 million people benefit from the global charity work of SOS Children's Villages, and our work in 133 countries around the world is vital to ensuring a better future for vulnerable children. You can help by sponsoring a child.

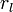 ). Simultaneously current will escape through the phospholipid bilayer (with resistance
). Simultaneously current will escape through the phospholipid bilayer (with resistance 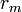 ) to the outside; and due to electrostatic forces a buildup of charge (
) to the outside; and due to electrostatic forces a buildup of charge (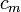 ) will take place along the bilayer.
) will take place along the bilayer.
